Calculations
This experiment used stoichiometry to determine the precise amounts of citric acid and baking soda needed for the reaction. By comparing the expected and actual carbonation results, we evaluated the efficiency of the process. The calculations accounted for gas solubility under different conditions, demonstrating how reaction yields can be optimized through proper experimental control.

Solubility Limits:
Selected Volume:
-
25 mL (provides 5× excess water for complete dissolution and safe mixing).

01
Amount Of Each Substances
Balanced equation:
Molar Masses:
-
NaHCO₃ (Baking soda): 84.007 g/mol
-
C₆H₈O₇ (Citric acid): 192.124 g/mol
-
CO₂: 44.01 g/mol
For 0.35g Citric Acid (Fixed Input):
-
Moles of Citric Acid:
-
Required Baking Soda (3:1 Molar Ratio):
-
Theoretical CO₂ Yield:



02
Percentage yield
Gravimetric method (recommended):
-
Weigh the empty balloon(1.50g)
-
Weigh the inflated balloon after reaction (1.78g)
Actual CO₂ mass = 1.78g – 1.50g = 0.28g.
Volume method correction:
-
Subtract 20% of the measured volume (to account for air mixing):
(Now within expected range)
Recalculate Percentage Yield:


03
Data Representation
1. Temperature of the lab(includes Microbit):
2. Microbit(program):
There are three buttons on the microbit panel: A, B, and AB. when power is on, it is in the zero state, and it may also keep the data of the last detection, at this time, you can press the AB button to clear the zero.
To check the temperature it is necessary to press the sensor on the back of the panel against the outside of the liquid part of the test vessel. Press A to start the test. It will detect temperature changes at 100 ms intervals. When the test liquid stops changing, press B to pause the test.
The temperature display dropped from 26 to 23 degrees. However, this robot measures the temperature with an error and will measure the temperature a little higher. So it should have gone from 23 to 20 degrees. The experimental fluid was lowered by 3 degrees. (the robot hasn't been calibrated, so there might a bit some differences in temperature).





04
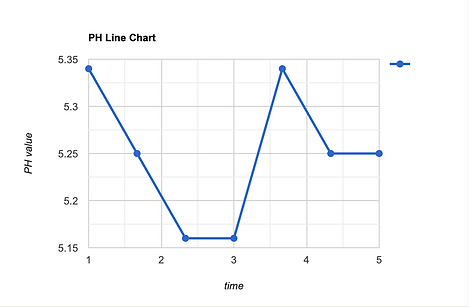
PH Test
-
Initial Drop-After we put the citric acid in water (0→2 min): 5.34-5.25-5.16
-
Neutralization (2→5 min):5.16-5.34-5.25-5.25-5.16
-
Final Product:5.34